Discover how Georgia’s specially designed instruction transforms classrooms into personalized learning environments that empower every student to succeed.
Understanding the Foundation of Specially Designed Instruction in Georgia
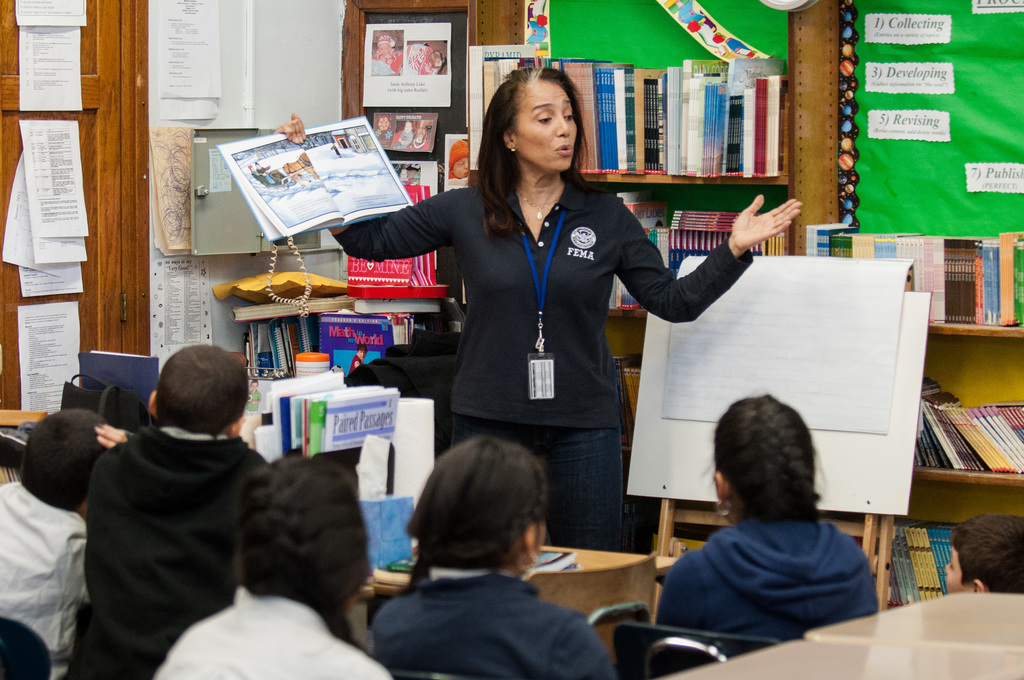
Georgia’s approach to special education is built on a comprehensive framework that prioritizes individualized learning experiences for students with disabilities. The state’s commitment to specially designed instruction (SDI) reflects a deep understanding that every student deserves an education tailored to their unique needs. Recent statistics show that approximately 12% of Georgia’s student population receives special education services, highlighting the critical importance of effective SDI implementation. The state’s educational framework emphasizes evidence-based practices, continuous assessment, and adaptive teaching strategies to ensure each student reaches their full potential. This foundation serves as a model for other states, demonstrating how personalized learning strategies can significantly impact student success rates and academic achievement.
Core Components of Specially Designed Instruction
- Systematic adaptation of curriculum content to match individual learning capabilities
- Modification of instructional methodology to accommodate diverse learning styles
- Customized delivery methods ensuring optimal comprehension and retention
- Integration of specialized support services and resources
- Regular progress monitoring and assessment adjustments
- Implementation of research-based instructional strategies
Classroom Implementation Strategies
Effective implementation of SDI in Georgia classrooms involves a multi-faceted approach that combines traditional teaching methods with innovative instructional techniques. Teachers employ various strategies such as explicit instruction, where concepts are broken down into manageable steps and taught systematically. Multi-sensory learning approaches have shown a 40% increase in student engagement when properly implemented. These strategies include visual aids, hands-on activities, and auditory learning tools that cater to different learning preferences. Pre-teaching key vocabulary and concepts has become a cornerstone of successful SDI implementation, with data showing improved comprehension rates of up to 35% when these techniques are consistently applied.
Technology Integration in Special Education
- Text-to-speech and speech-to-text applications for reading and writing support
- Adaptive learning software that adjusts to student progress
- Interactive whiteboards for visual and tactile learning experiences
- Mobile devices with specialized educational apps
- Assistive technology devices for various physical and cognitive needs
Assessment and Progress Monitoring
Georgia’s approach to assessment in special education emphasizes continuous monitoring and data-driven decision-making. Educators utilize a combination of formal and informal assessment tools to track student progress and adjust instruction accordingly. Recent studies indicate that schools implementing regular progress monitoring see a 25% improvement in student achievement outcomes. These assessments help identify areas where students need additional support and allow teachers to modify their instructional approaches in real-time.
Collaborative Teaching Models
The success of SDI in Georgia relies heavily on effective collaboration between general and special education teachers. Co-teaching models have become increasingly prevalent, with over 60% of Georgia schools now implementing some form of collaborative teaching. This approach ensures that students receive comprehensive support while maintaining access to the general education curriculum. Teachers work together to modify lessons, share expertise, and create inclusive learning environments that benefit all students.
Individualized Learning Environments
- Flexible seating arrangements to accommodate different learning styles
- Designated quiet spaces for independent work
- Sensory-friendly classroom modifications
- Visual schedules and organizational supports
- Accessible materials and resources
Behavioral Support and Social Skills Development
Georgia’s SDI framework incorporates comprehensive behavioral support systems and social skills training. Schools implement positive behavior intervention strategies (PBIS) and individualized behavior plans that have resulted in a 45% reduction in behavioral incidents across participating schools. Social skills instruction is integrated into daily routines, helping students develop essential life skills alongside academic achievements.
Success Stories and Best Practices
Across Georgia, numerous schools have demonstrated remarkable success with their SDI implementation. For example, one metro Atlanta school reported a 30% increase in special education students meeting grade-level standards after implementing comprehensive SDI strategies. These success stories often highlight the importance of consistent implementation, teacher training, and family engagement in the special education process.
Resources and Support Systems
- Professional development opportunities for educators
- Online learning platforms and digital resources
- Parent support networks and advocacy groups
- State-funded training programs and workshops
- Collaborative planning tools and resources
Future of Special Education in Georgia
The future of specially designed instruction in Georgia looks promising, with continued innovation and advancement in educational technologies and teaching methodologies. The state is investing in artificial intelligence-powered learning tools, expected to enhance personalized learning capabilities by 50% over the next five years. Additionally, increased focus on teacher training programs and professional development ensures that educators are well-equipped to meet the evolving needs of students with disabilities. As Georgia continues to lead in special education innovation, the emphasis remains on creating inclusive, effective, and personalized learning experiences for all students.
FAQ
What specially designed instruction is not?
That is, SDI is in addition to general education, not in lieu of it, and instruction that is for all students generally is not considered SDI. Further, SDI is individualized and based on information in the IEP, and it is intended to help that student master IEP goals and objectives.
What is SDI in a lesson plan?
Specially Designed Instruction (SDI) means adapting what is taught, the methodology and/or the manner in which instruction is provided to meet the student’s unique needs.
What does 4 out of 5 trials mean on an IEP?
The definition of performance criteria is the level the student must demonstrate for mastery (for example 80%) and the number of times that skill or behavior must be demonstrated to be considered proficient (for example 4 out of 5 trials).
What are the three components of specially designed instruction?
* Evidence of SDI must address at least one of the following: content, methodology, and delivery of instruction. Adapting any one of these three in isolation, however, may not constitute SDI.
Sources
[1] https://www.mdek12.org/sites/default/files/sdi_document.pdf
[2] https://digitalcommons.georgiasouthern.edu/gcld/2024/2024/2/
[3] https://www.glynn.k12.ga.us/apps/pages/index.jsp?uREC_ID=1727227&type=d&pREC_ID=2081978